1. Introduction
The generating function of Bernoulli polynomial is defined as:
2. Identities
2.1. Theorem of complement
Proof
therefore,
(1)
2.3. Theorem of multiplication
Proof
therefore,
(1)
multiplying and dividing by m , therefore
(2)
(3)
(4)
from (1) and (4),
(5)
therefore,
2.4. Theorem of hyperbolic-Bernoulli function
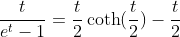
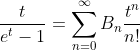
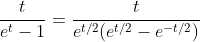
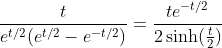
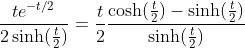
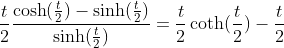
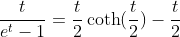
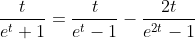
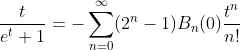
proof
therefore;
2.5. Theorem of exponential-Bernoulli function
based on (UI.ID.1)
and based on
therefore,
2.5. Theorem of Bernoulli polynomial in term of Bernoulli number
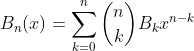
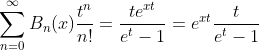
Proof
(1)
(2)
(3)
from (1) and (3) , therefore
equating the similar coefficients
2.6. Theorem of sum of nth powers


(1)
based on geometric series of exponential and taylor series of exponential function (GS.ID.2) (E.ID.1)
(2)
from (1) and (2)
(3)
from the definitions of Bernoulli polynomials and number (4)
from (3) and (4)
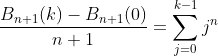
(5)
therefore,
(6)
(7)
(8)
(9)
2.6. Theorem of recurrence
subtracting (6) from (7) or (8) from (9) (above)
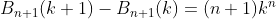
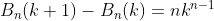
subtracting (6) from (7) or (8) from (9) (above)







No comments:
Post a Comment